Understanding the Cost of Mining 200 TPH Nickel Ore
Introduction to Nickel Ore Mining Costs
Nickel ore mining involves significant expenses, influenced by factors like extraction methods, labor, equipment, and logistics. A production rate of 200 tons per hour (TPH) requires substantial investment in machinery, energy, and operational efficiency. This article breaks down the key cost components involved in mining nickel ore at this scale.
Equipment and Machinery Expenses
Mining 200 TPH of nickel ore demands heavy-duty equipment such as excavators, haul trucks, crushers, and conveyors. The initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) for these machines can be substantial. Maintenance costs also add up over time due to wear and tear in harsh mining conditions. Energy consumption is another major factor, especially if operations rely on diesel-powered machinery or grid electricity in remote locations. 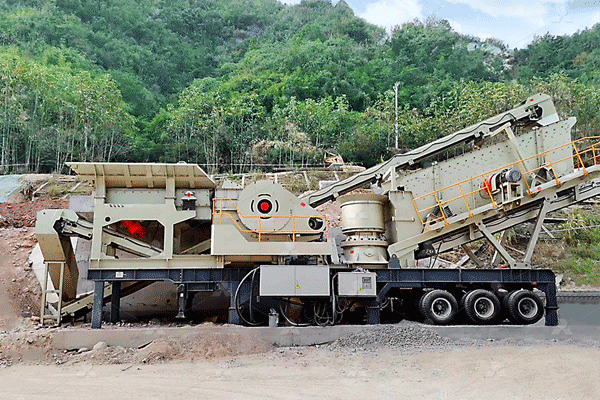
Labor and Operational Costs
Skilled labor is essential for efficient nickel ore extraction and processing. Wages for geologists, engineers, machine operators, and support staff contribute significantly to operational expenses. Additionally, safety measures and compliance with environmental regulations require additional staffing and training investments. Labor costs vary by region but typically account for a notable portion of the total budget.
Transportation and Logistics
Moving 200 TPH of nickel ore from the mine to processing facilities or export terminals involves high transportation costs. Depending on the mine’s location, expenses may include road transport, rail freight, or shipping. Fuel prices and infrastructure quality directly impact these costs. Remote mines often face higher logistical challenges due to limited access to ports or highways.
Processing and Refining Costs
After extraction, nickel ore undergoes beneficiation (crushing and grinding) before smelting or refining. These processes require specialized facilities with high energy consumption. If third-party processors are used, their service fees add to overall expenses. The choice between on-site processing and outsourcing depends on cost-benefit analysis based on production volume and market conditions. 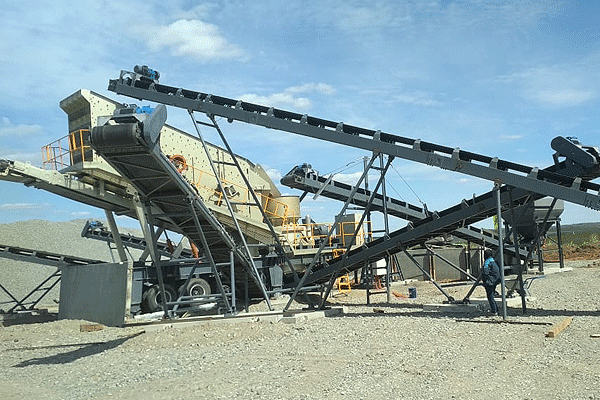
Environmental Compliance Costs
Mining operations must adhere to strict environmental regulations to minimize ecological damage. Compliance includes land rehabilitation, waste management systems, pollution control measures, and permits—all of which increase operational costs. Failure to meet regulatory standards can result in fines or project delays that further escalate expenses.
Market Conditions Impacting Costs
Nickel prices fluctuate based on global demand from industries like stainless steel production and electric vehicle batteries. When prices are high, mining becomes more profitable despite rising costs; during downturns, operations may scale back to reduce losses. Currency exchange rates also affect costs for imported equipment or exported ore.
Conclusion: Balancing Efficiency and Cost Control
Mining 200 TPH of nickel ore is a capital-intensive process requiring careful financial planning across multiple areas—equipment procurement, labor management, logistics optimization, regulatory compliance, and market adaptability. Companies must continuously assess cost-saving strategies while maintaining operational efficiency to remain competitive in the volatile nickel industry.
