200t/h Granite Crushing Plant for Hydropower Station
Introduction
Granite is a widely used construction material due to its durability, strength, and aesthetic appeal. In hydropower station projects, granite aggregates play a crucial role in concrete production, dam construction, and road base layers. A 200t/h granite crushing plant is designed to meet the high demand for quality aggregates while ensuring efficiency and environmental sustainability. This article explores the key aspects of such a crushing plant, including its design considerations, operational benefits, and environmental impact.
Design Considerations
A 200t/h granite crushing plant must be carefully designed to handle large volumes of hard rock efficiently. The primary components include a jaw crusher for coarse crushing, a cone crusher or impact crusher for secondary crushing, and vibrating screens for grading the final products.
The layout should minimize dust emissions and noise pollution while optimizing material flow. Additionally, automation systems can enhance productivity by monitoring feed rates, adjusting crusher settings, and detecting potential malfunctions. Proper maintenance access points should also be incorporated to reduce downtime during servicing.
Operational Benefits
One of the main advantages of a well-designed granite crushing plant is its ability to produce consistent aggregate sizes suitable for hydropower construction. High-capacity plants (200t/h) ensure uninterrupted supply even during peak demand periods.
Energy-efficient motors and optimized crushing chambers help reduce operational costs while maintaining high throughput. Furthermore, modular designs allow quick relocation if the project requires shifting work zones along the hydropower site. These features make such plants indispensable in large-scale infrastructure projects.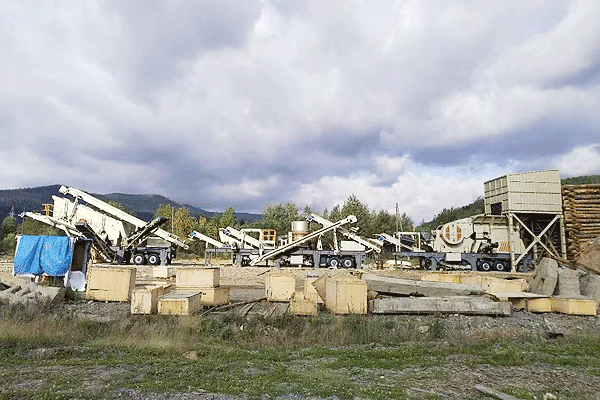 
Environmental Impact Mitigation
Crushing granite generates dust and noise, which can affect nearby communities if not managed properly. Modern plants incorporate water spray systems and enclosed conveyor belts to suppress dust emissions effectively. Noise barriers around crushers and screening units further minimize disturbances in sensitive areas. 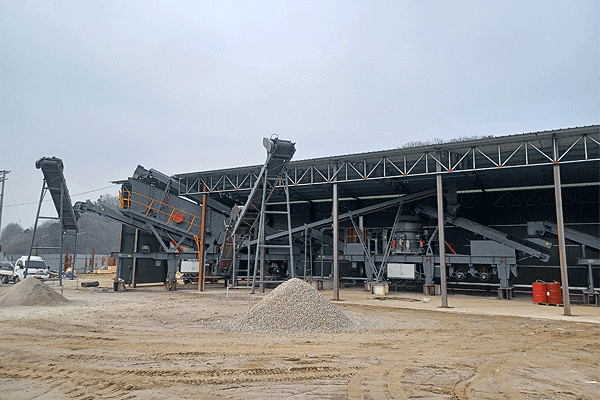
Recycling water used in dust suppression reduces consumption while sedimentation ponds prevent contaminated runoff from entering natural water sources—a critical consideration near hydropower stations where ecological balance must be preserved. Sustainable practices like these align with global environmental regulations while maintaining productivity standards.
Conclusion
A 200t/h granite crushing plant tailored for hydropower stations combines efficiency with sustainability—delivering high-quality aggregates without compromising environmental responsibility or operational reliability—making it an essential asset in modern infrastructure development projects worldwide!
