Lead-Zinc Ore Mobile Processing Plant: A Flexible Solution for Mining Operations
Introduction
The mining industry continues to evolve, with mobile processing plants becoming a game-changer for lead-zinc ore extraction. Unlike traditional fixed plants, these portable units offer flexibility, cost-efficiency, and rapid deployment. They are particularly useful in remote locations or short-term mining projects where permanent infrastructure is impractical. This article explores the key advantages, working principles, and applications of mobile lead-zinc ore processing plants.
Advantages of Mobile Processing Plants
Mobile processing plants provide several benefits over conventional setups. First, they reduce transportation costs by allowing on-site processing, minimizing the need to haul raw ore over long distances. Second, their modular design enables quick assembly and disassembly, making them ideal for temporary mining sites. Third, these plants have lower capital investment requirements compared to permanent facilities. Additionally, they can be relocated as mining operations shift, ensuring continuous production without significant downtime. 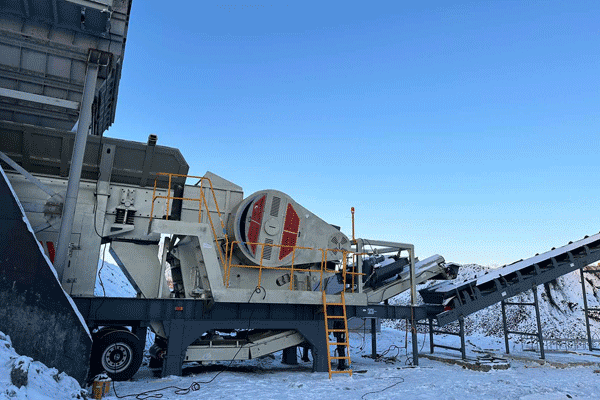
Key Components and Working Principle
A typical mobile lead-zinc ore processing plant includes crushing units, grinding mills, flotation cells, and dewatering systems. The process begins with crushing the ore into smaller particles before grinding it into a fine powder. The powdered ore then undergoes froth flotation to separate lead and zinc minerals from waste material. Finally, the concentrated minerals are dewatered for further refining or direct sale. Advanced models may incorporate automation for improved efficiency and real-time monitoring of operations.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Mobile processing plants contribute to sustainable mining practices by reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Their compact design minimizes land disturbance, while closed-loop water systems help conserve resources. Economically, they lower operational costs by eliminating the need for extensive infrastructure and long-distance ore transport. Furthermore, their adaptability allows miners to respond quickly to fluctuating market demands without committing to large-scale investments. 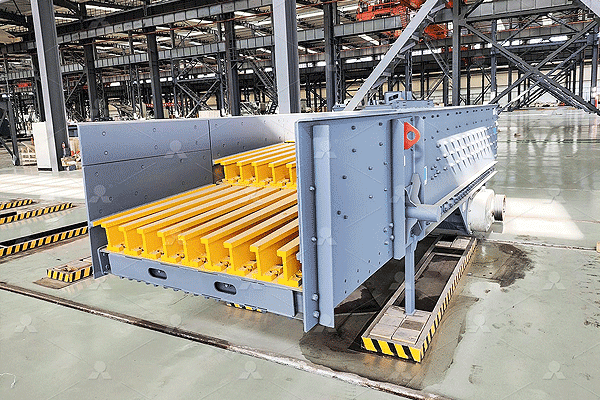
Applications in Modern Mining
These plants are widely used in small- to medium-scale mining operations where flexibility is crucial. They are also deployed in exploration projects to test ore viability before establishing permanent facilities. In regions with unstable power supplies or harsh climates, mobile units offer a reliable alternative due to their self-contained power systems and rugged construction. Some operators even use them for reprocessing tailings to recover residual metals sustainably.
Conclusion
The rise of mobile lead-zinc ore processing plants reflects the industry’s shift toward efficiency and sustainability. By combining portability with advanced mineral extraction techniques, these units provide a practical solution for diverse mining scenarios. As technology advances, further improvements in automation and energy efficiency will likely expand their role in modern mineral processing operations worldwide.
