Complete Guide for Choosing the Right Stone Crusher
Selecting the right stone crusher is crucial for optimizing productivity, reducing operational costs, and ensuring long-term efficiency in mining or construction projects. This guide provides key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
1. Understanding Different Types of Stone Crushers
Stone crushers come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
- Jaw Crushers: Ideal for primary crushing, handling large rocks with high compressive strength.
- Impact Crushers: Best for softer materials like limestone, producing uniform-shaped aggregates.
- Cone Crushers: Suitable for secondary or tertiary crushing, offering precise particle size control.
- Gyratory Crushers: Used in large-scale mining operations due to their high capacity.
- Roll Crushers: Effective for fine crushing and minimizing over-sized material.
Choosing the right type depends on material hardness, required output size, and production capacity.
2. Assessing Material Characteristics
The properties of the raw material significantly influence crusher selection:
- Hardness: Harder materials (e.g., granite) require robust crushers like jaw or gyratory models.
- Moisture Content: Wet or sticky materials may need specialized crushers to prevent clogging.
- Abrasiveness: Highly abrasive rocks wear out components faster; impact-resistant liners may be necessary.
Conducting a material test helps determine the most suitable crusher design and wear resistance requirements. 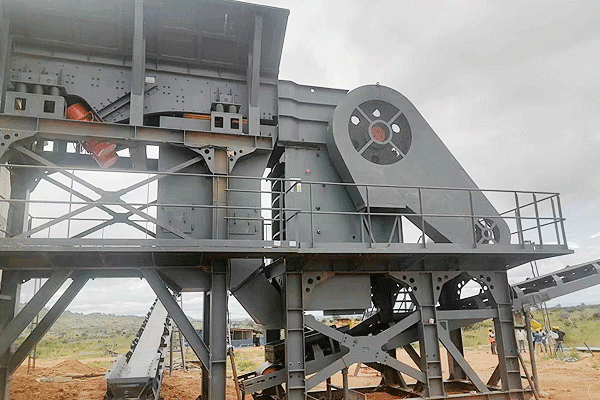
3. Determining Required Output Size
The desired final product size dictates crusher selection:
- Coarse aggregates (40mm+) typically use jaw or gyratory crushers.
- Medium-sized aggregates (20–40mm) work well with cone or impact crushers.
- Fine aggregates (<5mm) may require vertical shaft impactors or roll crushers for shaping and grading.
If multiple stages of crushing are needed, consider a combination of primary, secondary, and tertiary units for optimal results.
4. Evaluating Production Capacity Needs
Production requirements vary based on project scale: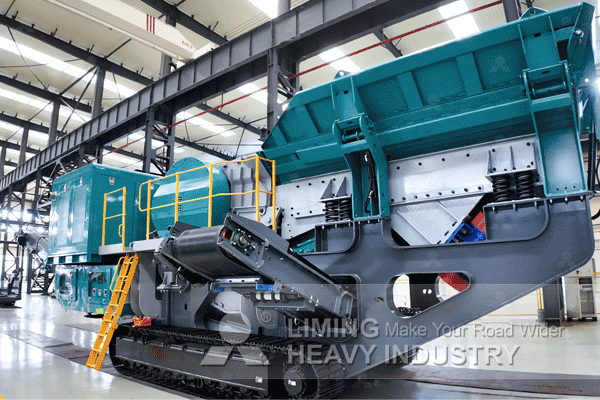 
- Small-scale operations (<100 tons/hour) can use compact jaw or cone crushers.
- Medium-scale projects (100–500 tons/hour) benefit from higher-capacity cone or impact models.
- Large-scale mining (>500 tons/hour) demands gyratory crushers or multi-stage setups with screening systems accurately matched to throughput demands avoids bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processing lines.
5 Considering Maintenance And Operational Costs
Operating expenses play a major role in long-term profitability:
- Wear part replacement frequency affects downtime costs; choose machines with easily accessible components.
- Energy consumption varies between models; efficient designs reduce electricity bills over time.
- Automation features (e.g., hydraulic adjustments) minimize manual labor while improving safety.
Investing upfront in durable machinery lowers lifetime ownership costs despite higher initial prices.
Conclusion
Selecting an appropriate stone-crushing solution requires analyzing material properties output specifications production volume budgets By carefully evaluating these factors operators ensure optimal performance cost-efficiency sustainability across various applications
