Indonesia 280-320TPH Andesite Crushing Plant: Key Features and Applications
Introduction to Andesite Crushing
Andesite is a common volcanic rock with medium hardness, widely used in construction, road building, and infrastructure projects. Due to its durability and resistance to wear, it is a preferred material for high-quality aggregates. A crushing plant with a capacity of 280-320 tons per hour (TPH) is ideal for large-scale projects requiring consistent output and efficiency.
This article explores the key aspects of such a crushing plant, including equipment selection, workflow optimization, and maintenance considerations. Each section provides standalone insights for professionals in the mining and construction industries.
Equipment Configuration for High Efficiency
A 280-320TPH andesite crushing plant typically includes primary, secondary, and tertiary crushing stages. The primary crusher—often a jaw crusher—breaks large rocks into manageable sizes. Secondary crushing may involve a cone crusher or impact crusher to further refine the material. Finally, vibrating screens separate the crushed stone into different sizes for various applications.
Advanced automation systems ensure smooth operation by monitoring feed rates, power consumption, and potential blockages. Dust suppression systems are also essential to comply with environmental regulations while maintaining worker safety.
Optimizing Workflow for Maximum Output
Efficient workflow design minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity. Properly sized conveyors transport material between crushing stages without bottlenecks. Stockpiling crushed aggregates before final screening helps balance production flow when demand fluctuates. 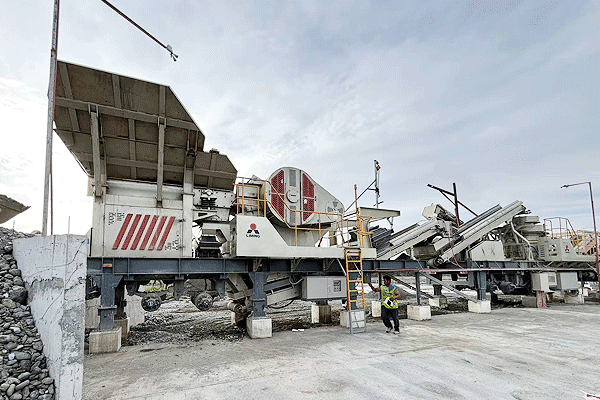
Regular calibration of crushers ensures consistent particle size distribution, which is crucial for meeting project specifications. Additionally, real-time monitoring tools allow operators to adjust settings remotely, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency.
Maintenance Strategies for Longevity
Preventive maintenance is critical in high-capacity crushing plants to avoid unexpected breakdowns. Key components such as bearings, belts, and liners should be inspected frequently. Lubrication schedules must be strictly followed to reduce wear on moving parts.
Predictive maintenance techniques—such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging—can detect early signs of equipment failure before they escalate into costly repairs. Keeping spare parts readily available further minimizes downtime during maintenance cycles.
Environmental Considerations
Crushing plants must adhere to local environmental regulations to minimize their ecological impact. Dust control measures—including water sprays and enclosed conveyor systems—help reduce airborne particles. Noise barriers may also be required near residential areas to mitigate operational disturbances. 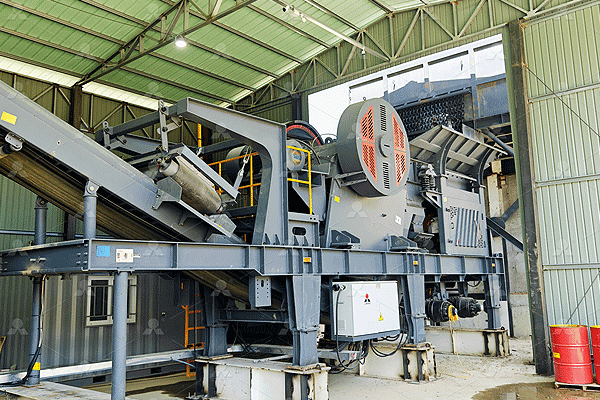
Recycling water used in dust suppression systems conserves resources while ensuring compliance with sustainability standards. Proper waste management practices ensure that non-recyclable byproducts are disposed of responsibly.
Conclusion
A well-designed 280-320TPH andesite crushing plant delivers high efficiency, durability, and compliance with environmental standards. By selecting the right equipment, optimizing workflows, implementing proactive maintenance strategies, and adhering to sustainability guidelines, operators can achieve long-term success in large-scale aggregate production. Whether supplying materials for highways or commercial construction projects, such a plant plays a vital role in modern infrastructure development.
